Spring作为当前Java最流行、最强大的轻量级框架,受到了程序员的热烈欢迎。
准确的了解Spring Bean的生命周期是非常必要的。我们通常使用ApplicationContext作为Spring容器。这里,我们讲的也是 ApplicationContext中Bean的生命周期。而实际上BeanFactory也是差不多的,只不过处理器需要手动注册。
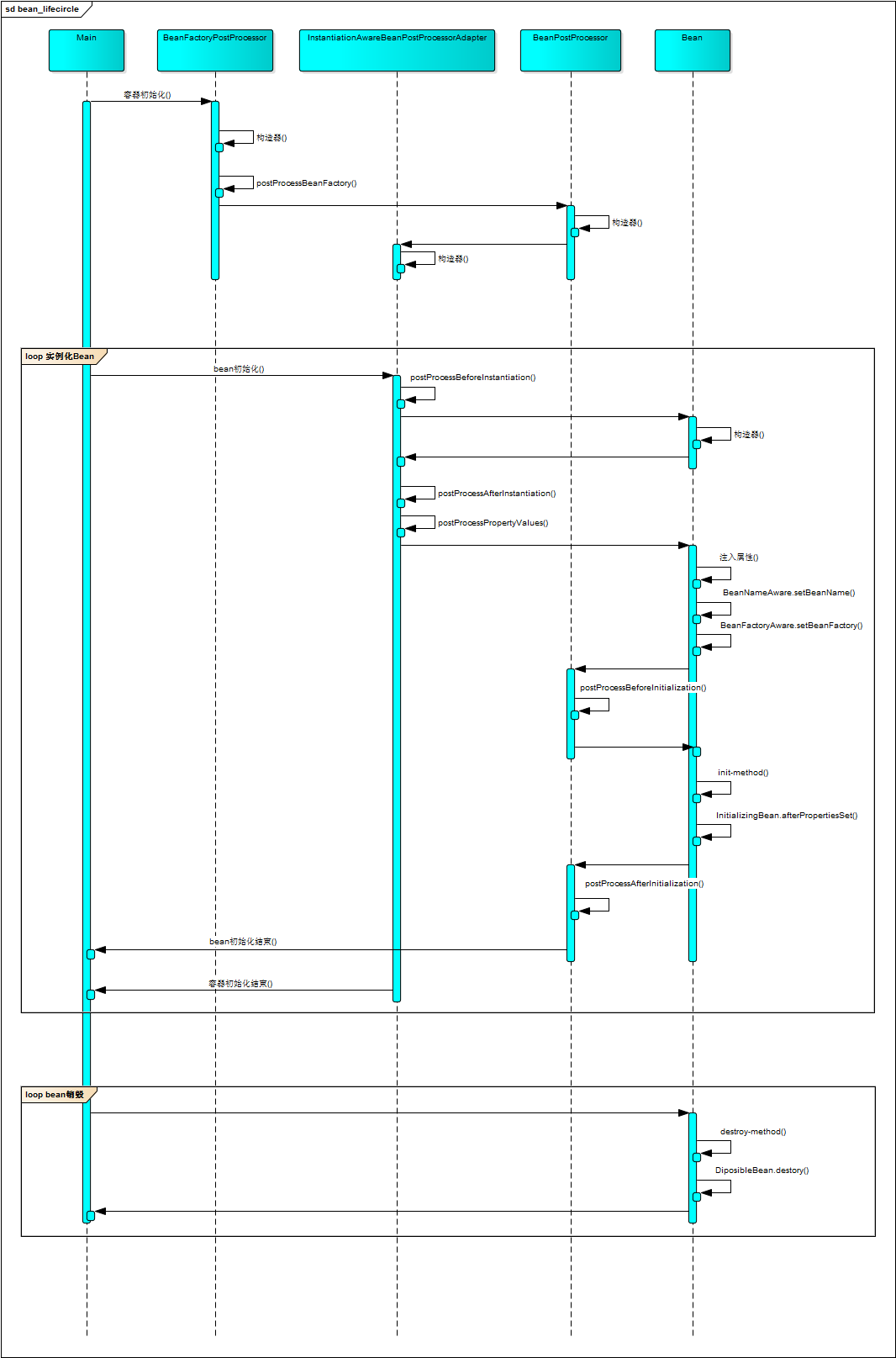
生命周期时序图
Spring Bean的完整生命周期从创建Spring容器开始,直到最终Spring容器销毁Bean,这其中包含了一系列关键点。
![]()
接口方法分类
Bean的完整生命周期经历了各种方法调用,这些方法可以划分为以下几类:
- Bean自身的方法:这个包括了Bean本身调用的方法和通过配置文件中的
init-method和destroy-method指定的方法 - Bean级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了
BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean和DiposableBean这些接口的方法 - 容器级生命周期接口方法:这个包括了
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 BeanPostProcessor 这两个接口实现,一般称它们的实现类为后处理器。 - 工厂后处理器接口方法:这个包括了
AspectJWeavingEnabler, ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, CustomAutowireConfigurer等等非常有用的工厂后处理器接口的方法,工厂后处理器也是容器级的,在应用上下文装配配置文件之后立即调用。
演示
我们用一个简单的Spring Bean来演示一下Spring Bean的生命周期。
- 首先是一个简单的Spring Bean,调用Bean自身的方法和Bean级生命周期接口方法,为了方便演示,它实现了BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean和DiposableBean这4个接口,同时有2个方法,对应配置文件中的init-method和destroy-method。如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| package springBeanTest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware,
InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
private String address;
private int phone;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private String beanName;
public Person() {
System.out.println("【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性name");
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性address");
this.address = address;
}
public int getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(int phone) {
System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性phone");
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [address=" + address + ", name=" + name + ", phone="
+ phone + "]";
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()");
this.beanFactory = arg0;
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String arg0) {
System.out.println("【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()");
this.beanName = arg0;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out
.println("【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
public void myDestory() {
System.out.println("【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法");
}
}
|
2、接下来是演示BeanPostProcessor接口的方法,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| package springBeanTest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public MyBeanPostProcessor() {
super();
System.out.println("这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改!");
return arg0;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改!");
return arg0;
}
}
|
如上,BeanPostProcessor接口包括2个方法postProcessAfterInitialization和postProcessBeforeInitialization,这两个方法的第一个参数都是要处理的Bean对象,第二个参数都是Bean的name。返回值也都是要处理的Bean对象。这里要注意。
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口本质是BeanPostProcessor的子接口,一般我们继承Spring为其提供的适配器类InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor Adapter来使用它,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package springBeanTest;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter;
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter {
public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() {
super();
System.out
.println("这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass,
String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法");
return null;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs,
PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法");
return pvs;
}
}
|
这个有3个方法,其中第二个方法postProcessAfterInitialization就是重写了BeanPostProcessor的方法。第三个方法postProcessPropertyValues用来操作属性,返回值也应该是PropertyValues对象。
- 演示工厂后处理器接口方法,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package springBeanTest;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor() {
super();
System.out.println("这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!!");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory arg0)
throws BeansException {
System.out
.println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法");
BeanDefinition bd = arg0.getBeanDefinition("person");
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("phone", "110");
}
}
|
- 配置文件如下beans.xml,很简单,使用ApplicationContext,处理器不用手动注册:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd">
<bean id="beanPostProcessor" class="springBeanTest.MyBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
<bean id="instantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" class="springBeanTest.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor">
</bean>
<bean id="beanFactoryPostProcessor" class="springBeanTest.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor">
</bean>
<bean id="person" class="springBeanTest.Person" init-method="myInit"
destroy-method="myDestory" scope="singleton" p:name="张三" p:address="广州"
p:phone="15900000000" />
</beans>
|
- 下面测试一下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package springBeanTest;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BeanLifeCycle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("现在开始初始化容器");
ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("springBeanTest/beans.xml");
System.out.println("容器初始化成功");
Person person = factory.getBean("person",Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println("现在开始关闭容器!");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).registerShutdownHook();
}
}
|
关闭容器使用的实际是AbstractApplicationContext的钩子方法。
控制台输出:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| 现在开始初始化容器
2014-5-18 15:46:20 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@19a0c7c: startup date [Sun May 18 15:46:20 CST 2014]; root of context hierarchy
2014-5-18 15:46:20 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions
信息: Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [springBeanTest/beans.xml]
这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!!
BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法
这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!
这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!!
2014-5-18 15:46:20 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory preInstantiateSingletons
信息: Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@9934d4: defining beans [beanPostProcessor,instantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,beanFactoryPostProcessor,person]; root of factory hierarchy
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法
【注入属性】注入属性address
【注入属性】注入属性name
【注入属性】注入属性phone
【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()
【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()
BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改!
【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()
【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法
BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改!
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法
容器初始化成功
Person [address=广州, name=张三, phone=110]
现在开始关闭容器!
【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()
【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法
|